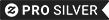Tap / click on image to see more RealViewsTM
$83.95
per poster
VICTORY! CONGRESS PASSES DAYLIGHT SAVING BILL POSTER
Qty:
Choose Your Format
Size
Custom (51.49cm x 91.44cm)
Border
None
About Posters
Sold by
About This Design
VICTORY! CONGRESS PASSES DAYLIGHT SAVING BILL POSTER
CONGRESS PASSES DAYLIGHT SAVING BILL" showing Uncle Sam turning a clock to daylight saving time as a clock-headed figure throws his hat in the air. The clock face of the figure reads "ONE HOUR OF EXTRA DAYLIGHT". The bottom caption says "Get Your Hoe Ready!" Daylight saving time (DST; also summer time in British English—see Terminology) is the practice of advancing clocks so that afternoons have more daylight and mornings have less. Typically clocks are adjusted forward one hour near the start of spring and are adjusted backward in autumn. Modern DST was first proposed in 1895 by George Vernon Hudson, a New Zealand entomologist. Many countries have used it since then; details vary by location and change occasionally. The practice is controversial. Adding daylight to afternoons benefits retailing, sports, and other activities that exploit sunlight after working hours, but causes problems for farming, evening entertainment and other occupations tied to the sun. Traffic fatalities are reduced when there is extra afternoon daylight; its effect on health and crime is less clear. Although an early goal of DST was to reduce evening usage of incandescent lighting, formerly a primary use of electricity, modern heating and cooling usage patterns differ greatly, and research about how DST currently affects energy use is limited and often contradictory. DST's occasional clock shifts present other challenges. They complicate timekeeping, and can disrupt meetings, travel, billing, recordkeeping, medical devices, heavy equipment, and sleep patterns. Often, software can adjust computer clocks automatically, but this can be limited and error-prone, particularly when DST rules change. Although not punctual in the modern sense, ancient civilisations adjusted daily schedules to the sun more flexibly than modern DST does, often dividing daylight into twelve equal hours regardless of day length, so that each daylight hour was longer during summer. For example, Roman water clocks had different scales for different months of the year: at Rome's latitude the third hour from sunrise, hora tertia, started by modern standards at 09:02 solar time and lasted 44 minutes at the winter solstice, but at the summer solstice it started at 06:58 and lasted 75 minutes. After ancient times, equal-length civil hours eventually supplanted unequal, so civil time no longer varies by season. Unequal hours are still used in a few traditional settings, such as some Mount Athos monasteries and some Jewish ceremonies. During his time as an American envoy to France, Benjamin Franklin, author of the proverb, "Early to bed, and early to rise, makes a man healthy, wealthy and wise", anonymously published a letter suggesting that Parisians economise on candles by rising earlier to use morning sunlight. This 1784 satire proposed taxing shutters, rationing candles, and waking the public by ringing church bells and firing cannons at sunrise. Franklin did not propose DST; like ancient Rome, 18th-century Europe did not keep precise schedules. However, this soon changed as rail and communication networks came to require a standardisation of time unknown in Franklin's day. Modern DST was first proposed by the New Zealand entomologist George Vernon Hudson, whose shift-work job gave him leisure time to collect insects, and made him aware of the value of after-hours daylight. In 1895 he presented a paper to the Wellington Philosophical Society proposing a two-hour daylight-saving shift, and after considerable interest was expressed in Christchurch, New Zealand he followed up in an 1898 paper. Many publications incorrectly credit DST's invention to the prominent English builder and outdoorsman William Willett, who independently conceived DST in 1905 during a pre-breakfast ride, when he observed with dismay how many Londoners slept through a large part of a summer day. An avid golfer, he also disliked cutting short his round at dusk. His solution was to advance the clock during the summer months, a proposal he published two years later. As described in Politics below, Willett lobbied unsuccessfully for the proposal in the UK until his death in 1915, and Germany, its World War I allies, and their occupied zones were the first European nations to use Willett's invention, starting April 30, 1916, as a way to conserve coal during wartime. Britain, most of its allies, and many European neutrals soon followed suit. Russia and a few other countries waited until the next year; and the United States adopted it in 1918. Since then, the world has seen many enactments, adjustments, and repeals. Daylight saving has caused controversy since it began. Winston Churchill argued that it enlarges "the opportunities for the pursuit of health and happiness among the millions of people who live in this country". Robertson Davies, however, detected "the bony, blue-fingered hand of Puritanism, eager to push people into bed earlier, and get them up earlier, to make them healthy, wealthy and wise in spite of themselves", and wags have dubbed it "Daylight Slaving Time". Historically, retailing, sports and tourism interests have favored daylight saving, while agricultural and evening entertainment interests have opposed it, and its initial adoption has been prompted by energy crisis and war. The fate of Willett's 1907 proposal illustrates several political issues involved. The proposal attracted many supporters, including Balfour, Churchill, Lloyd George, MacDonald, Edward VII (who used half-hour DST at Sandringham), the managing director of Harrods, and the manager of the National Bank. However, the opposition was stronger: it included Prime Minister Asquith, Christie (the Astronomer Royal), George Darwin, Napier Shaw (director of the Meteorological Office), many agricultural organisations, and theatre owners. After many hearings the proposal was narrowly defeated in a Parliament committee vote in 1909. Willett's allies introduced similar bills every year from 1911 through 1914, to no avail. The U.S. was even more sceptical: Andrew Peters introduced a DST bill to the U.S. House of Representatives in May 1909, but it soon died in committee. Retailers generally favour DST. United Cigar Stores hailed a 1918 DST bill. World War I changed the political equation, as DST was promoted as a way to alleviate hardships from wartime coal shortages and air raid blackouts. After Germany led the way, the United Kingdom first used DST on May 21, 1916. U.S. retailing and manufacturing interests led by Pittsburgh industrialist Robert Garland soon began lobbying for DST, but were opposed by railroads. The U.S.'s 1917 entry to the war overcame objections, and DST was established in 1918. The war's end swung the pendulum back. Farmers continued to dislike DST, and many countries repealed it after the war. Britain was an exception: it retained DST nationwide but over the years adjusted transition dates for several reasons, including special rules during the 1920s and 1930s to avoid clock shifts on Easter mornings. The U.S. was more typical: Congress repealed DST after 1919. President Woodrow Wilson, like Willett an avid golfer, vetoed the repeal twice but his second veto was overridden. Only a few U.S. cities retained DST locally thereafter, including New York so that its financial exchanges could maintain an hour of arbitrage trading with London, and Chicago and Cleveland to keep pace with New York. Wilson's successor Warren G. Harding opposed DST as a "deception". Reasoning that people should instead get up and go to work earlier in the summer, he ordered District of Columbia federal employees to start work at 08:00 rather than 09:00 during summer 1922. Many businesses followed suit though many others did not; the experiment was not repeated. Since Willett's day the world has seen many enactments, adjustments, and repeals of DST, with similar politics involved. The history of time in the United States includes DST during both world wars, but no standardisation of peacetime DST until 1966. In the mid-1980s, Clorox (parent of Kingsford Charcoal) and 7-Eleven provided the primary funding for the Daylight Saving Time Coalition behind the 1987 extension to U.S. DST, and both Idaho senators voted for it based on the premise that during DST fast-food restaurants sell more French fries, which are made from Idaho potatoes; in 2005, the Sporting Goods Manufacturers Association and the National Association of Convenience Stores successfully lobbied for the 2007 extension to U.S. DST. After a three-year trial, 55% of Western Australians voted against DST in 2009, with urban areas split evenly and rural areas strongly opposed; it was the fourth consecutive referendum since 1975 to reject DST. In the UK the sport and leisure industry supports a proposal to observe SDST's additional hour year-round.
Customer Reviews
4.8 out of 5 stars rating14.5K Total Reviews
14,514 Reviews
Reviews for similar products
5 out of 5 stars rating
By Jubelen P.27 February 2020 • Verified Purchase
Print, Size: 76.20cm x 50.80cm, Media: Value Poster Paper (Semi-Gloss)
Zazzle Reviewer Program
my staff loves it , and other branch is asking me where i got this and i give your website to them.
maybe you can add up on personalised option, laminated or a frame maybe . great job. but you can add an option if we wanted to have it laminated or frame as add up option
5 out of 5 stars rating
By Timothy G.14 October 2021 • Verified Purchase
Zazzle Reviewer Program
I hung this in the stairwell of our house, near some other Renoir pictures. My daughter says it looks like she is looking at her when she walks up the stairs.
it's called "The Excursionist", she is holding a walking stick. Renoir was an impressionist, I don't think this is an actual person. The finished framed picture arrived and looks better than the online pic - Beautiful!
5 out of 5 stars rating
By Ross Y.31 December 2019 • Verified Purchase
Print, Size: 48.26cm x 33.02cm, Media: Value Poster Paper (Semi-Gloss)
Zazzle Reviewer Program
Absolutely superb Art Deco poster. The colours are vibrant, sympathetic to the era and perfect for use. I framed it and hung above the entrance to my Art Deco inspired lounge room. Stunning! The print is precise, clear and of an excellent standard. It was cleverly packaged so there wasn’t a blemish or crease. Perfect!
Tags
Other Info
Product ID: 228961106942620223
Added on 16/7/09, 8:40 am
Rating: G
Recently Viewed Items