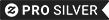Tap / click on image to see more RealViewsTM
$7.95
per card
Official Coat of Arms of George Washington Family
Qty:
Choose Your Format
Paper Type
Signature Matte
- 17 pt thickness / 120 lb weight
- Light white, uncoated matte finish with an eggshell texture
-$0.35
+$1.10
+$1.10
About Cards
Sold by
About This Design
Official Coat of Arms of George Washington Family
Historic arms used by the Washington family. . George Washington (February 22, 1732 [O.S. February 11, 1731]– December 14, 1799) served as the first President of the United States from 1789 to 1797 and as the commander of the Continental Army in the American Revolutionary War from 1775 to 1783. Because of his significant role in the revolution and in the formation of the United States, he is often referred to as "Father of His Country". The Continental Congress appointed Washington commander-in-chief of the American revolutionary forces in 1775. The following year, he forced the British out of Boston, lost New York City, and crossed the Delaware River in New Jersey, defeating the surprised enemy units later that year. Because of his strategy, Revolutionary forces captured the two main British combat armies at Saratoga and Yorktown. Negotiating with Congress, the colonial states, and French allies, he held together a tenuous army and a fragile nation amid the threats of disintegration and failure. Following the end of the war in 1783, King George III asked what Washington would do next and was told of rumours that he'd return to his farm; this prompted the king to state, "If he does that, he will be the greatest man in the world." Washington did return to private life and retired to his plantation at Mount Vernon. He presided over the Philadelphia Convention that drafted the United States Constitution in 1787 because of general dissatisfaction with the Articles of Confederation. Washington became President of the United States in 1789 and established many of the customs and usages of the new government's executive department. He sought to create a nation capable of surviving in a world torn asunder by war between Britain and France. His unilateral Proclamation of Neutrality of 1793 provided a basis for avoiding any involvement in foreign conflicts. He supported plans to build a strong central government by funding the national debt, implementing an effective tax system, and creating a national bank. Washington avoided the temptation of war and a decade of peace with Britain began with the Jay Treaty in 1795; he used his prestige to get it ratified over intense opposition from the Jeffersonians. Although never officially joining the Federalist Party, he supported its programs and was its inspirational leader. Washington's farewell address was a primer on republican virtue and a stern warning against partisanship, sectionalism, and involvement in foreign wars. He was awarded the first Congressional Gold Medal with the Thanks of Congress in 1776. Washington died in 1799. Henry Lee, delivering the funeral oration, declared Washington "first in war, first in peace, and first in the hearts of his countrymen". Historical scholars consistently rank him as one of the greatest United States presidents. Historically, they were used by knights to identify them apart from enemy soldiers. In Continental Europe, commoners were able to adopt burgher arms. Unlike seals and emblems, coats of arms have a formal description that is expressed as a blazon. In the 21st century, coats of arms are still in use by a variety of institutions and individuals (for example several universities have guidelines on how their coats of arms may be used and protect their use). The art of designing, displaying, describing and recording arms is called heraldry. The use of coats of arms by countries, states, provinces, towns and villages is called civic heraldry. In the heraldic traditions of England and Scotland an individual, rather than a family, had a coat of arms. In those traditions coats of arms are legal property transmitted from father to son; wives and daughters could also bear arms modified to indicate their relation to the current holder of the arms. Undifferenced arms are used only by one person at any given time. Other descendants of the original bearer could bear the ancestral arms only with some difference: usually a colour change or the addition of a distinguishing charge. One such charge is the label, which in British usage (outside the Royal Family) is now always the mark of an heir apparent. Because of their importance in identification, particularly in seals on legal documents, the use of arms was strictly regulated; few countries continue in this today. This has been carried out by heralds and the study of coats of arms is therefore called "heraldry". Some other traditions (e.g., Polish heraldry) are less restrictive — allowing, for example, all members of a dynastic house or family to use the same arms, although one or more elements may be reserved to the head of the house. In time, the use of arms spread from military entities to educational institutes, and other establishments. According to a design institute article, "The modern logo and corporate livery have evolved from the battle standard and military uniform of mediaeval times". In his book, The Visual Culture of Violence in the Late Middle Ages, Valentin Groebner argues that the images composed on coats of arms are in many cases designed to convey a feeling of power and strength, often in military terms. The author Helen Stuart argues that some coats of arms were a form of corporate logo. Museums on mediaeval armoury also point out that as emblems they may be viewed as precursors to the corporate logos of modern society, used for group identity formation. Note that not all personal or corporate insignia are heraldic, though they may share many features. For example, flags are used to identify ships (where they are called ensigns), embassies and such, and they use the same colours and designs found in heraldry, but they are not usually considered to be heraldic. A country may have both a national flag and a national coat of arms, and the two may not look alike at all. For example, the flag of Scotland (St Andrew's Cross) has a white saltire on a blue field, but the royal arms of Scotland has a red lion within a double tressure on a gold (or) field. The Great Seal of the United States is often said to be the coat of arms of the United States. The blazon ("Paleways of 13 pieces, argent and gules; a chief, azure") is intentionally to preserve the symbolic number 13. Most American states generally have seals, which fill the role of a coat of arms. However, the state of Vermont (founded as the independent Vermont Republic) follows the American convention of assigning use of a seal for authenticating official state documents and also has its own separate coat of arms. Many American social fraternities and sororities, especially college organisations, use coats of arms in their symbolism. These arms vary widely in their level of adherence to European heraldic tradition. Organisations formed outside the United States with U.S. membership also may have a coat of arms. Roman Catholic dioceses and cathedrals have a coat of arms.
Customer Reviews
4.9 out of 5 stars rating7.4K Total Reviews
7,387 Reviews
Reviews for similar products
5 out of 5 stars rating
By E.15 November 2021 • Verified Purchase
Folded Card, Size: Standard (12.7 cm x 17.8 cm), Paper: Signature Matte
Zazzle Reviewer Program
Lovely quality cards. Nice to get a real traditional Chrismassy theme in Australia, not the beach and Australian animals stuff. Excellent, would use again
5 out of 5 stars rating
By Angela M.16 November 2022 • Verified Purchase
Folded Card, Size: Big (21.6 cm x 28 cm), Paper: Signature Matte
Zazzle Reviewer Program
Easy to order
Good price
Quick delivery. Card came out exactly as ordered
5 out of 5 stars rating
By Nicole B.20 August 2025 • Verified Purchase
Folded Card, Size: Small (10.2 cm x 14.2 cm), Paper: Signature Matte
Very impressed with the quality of my personalised birthday card. Also received it very quickly .
Tags
Other Info
Product ID: 137337205760990069
Added on 22/2/10, 6:32 am
Rating: G
Recently Viewed Items