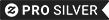Tap / click on image to see more RealViewsTM
$3.30
per postcard
Macau Official Coat Of Arms Heraldry Symbol Postcard
Qty:
Paper Type
Signature Matte
18 pt thickness / 120 lb weight Soft white, soft eggshell texture
-$0.35
Attribution
About Postcards
Sold by
About This Design
Macau Official Coat Of Arms Heraldry Symbol Postcard
Historically, they were used by knights to identify them apart from enemy soldiers. In Continental Europe, commoners were able to adopt burgher arms. Unlike seals and emblems, coats of arms have a formal description that is expressed as a blazon. In the 21st century, coats of arms are still in use by a variety of institutions and individuals (for example several universities have guidelines on how their coats of arms may be used and protect their use). The art of designing, displaying, describing and recording arms is called heraldry. The use of coats of arms by countries, states, provinces, towns and villages is called civic heraldry. In the heraldic traditions of England and Scotland an individual, rather than a family, had a coat of arms. In those traditions coats of arms are legal property transmitted from father to son; wives and daughters could also bear arms modified to indicate their relation to the current holder of the arms. Undifferenced arms are used only by one person at any given time. Other descendants of the original bearer could bear the ancestral arms only with some difference: usually a colour change or the addition of a distinguishing charge. One such charge is the label, which in British usage (outside the Royal Family) is now always the mark of an heir apparent. Because of their importance in identification, particularly in seals on legal documents, the use of arms was strictly regulated; few countries continue in this today. This has been carried out by heralds and the study of coats of arms is therefore called "heraldry". Some other traditions (e.g., Polish heraldry) are less restrictive — allowing, for example, all members of a dynastic house or family to use the same arms, although one or more elements may be reserved to the head of the house. In time, the use of coat of arms spread from military entities to educational institutes, and other establishments. According to a design institute article, "The modern logo and corporate livery have evolved from the battle standard and military uniform of mediaeval times". In his book, The Visual Culture of Violence in the Late Middle Ages, Valentin Groebner argues that the images composed on coats of arms are in many cases designed to convey a feeling of power and strength, often in military terms. The author Helen Stuart argues that some coat of arms were a form of corporate logo. Museums on mediaeval coat of arms also point out that as emblems they may be viewed as a pre-cursors to the corporate logos of modern society, used for group identity formation. The American Great Seal is often said to be the coat of arms of the United States. The blazon ("Paleways of 13 pieces, argent and gules; a chief, azure") is intentionally improper to preserve the symbolic number 13. Most American states generally have seals, which fill the role of a coat of arms. However, the state of Vermont (founded as the independent Vermont Republic) follows the American convention of assigning use of a seal for authenticating official state documents and also has its own separate coat of arms. Many American social fraternities and sororities, especially college organisations, use coats of arms in their symbolism. These arms vary widely in their level of adherence to European heraldic tradition. Organisations formed outside the United States with U.S. membership also may have a coat of arms. Roman Catholic dioceses and cathedrals have a coat of arms. Note that not all personal or corporate insignia are heraldic, though they may share many features. For example, flags are used to identify ships (where they are called ensigns), embassies and such, and they use the same colours and designs found in heraldry, but they are not usually considered to be heraldic. A country may have both a national flag and a national coat of arms, and the two may not look alike at all. For example, the flag of Scotland (St Andrew's Cross) has a white saltire on a blue field, but the royal arms of Scotland has a red lion within a double tressure on a gold (or) field. The Vatican has its own coat of arms. As the Papacy is not hereditary, its occupants display their personal arms combined with those of their office. Some Popes came from armigerous (noble) families; others adopted coats of arms during their career in the church. The latter typically allude to their ideal of life, or to specific Pontifical programmes.[11] A well known and widely displayed example in recent times was Pope John Paul II's coat of arms. His selection of a large letter M (for Mary) on his coat of arms was intended to express the message of his strong Marian devotion. Roman Catholic Dioceses also are assigned a coat of arms. A Basilica, or papal church also gets a coat of arms, which is usually displayed on the building. These may be used in countries which otherwise do not use heraldic devices. In Scotland, the Lord Lyon King of Arms has criminal jurisdiction to enforce the laws of arms. In England, Northern Ireland and Wales the use of arms is a matter of civil law and regulated from the College of Arms. In reference to a dispute over the exercise of authority over the Officers of Arms, Arthur Annesley, 1st Earl of Anglesey, Lord Privy Seal, declared on 16 June 1673 that the powers of the Earl Marshal were "to order, judge, and determine all matters touching arms, ensigns of nobility, honour, and chivalry; to make laws, ordinances, and statutes for the good government of the Officers of Arms; to nominate Officers to fill vacancies in the College of Arms; to punish and correct Officers of Arms for misbehaviour in the execution of their places". It was further declared that no patents of arms or any ensigns of nobility should be granted and no augmentation, alteration, or addition should be made to arms without the consent of the Earl Marshal. Today, the term "coat of arms" is frequently applied in two different ways. In some uses, it may indicate a full achievement of arms or heraldic achievement, which includes a variety of elements — usually a crest sitting atop a helmet, itself sitting on a shield; other common elements include supporters holding up the shield and a motto (beneath in England, above in Scotland). Some people wrongly use "coat of arms" or "arms" to refer to the escutcheon (i.e., the shield itself), or to one of several designs that may be combined in one shield. (Note that the crest is one specific part of a heraldic achievement and that "crest of arms" is a misnomer.) The "coat of arms" frequently are adorned with a device - a motto, emblem, or other mark used to distinguish the bearer from others. If a motto is a part of the achievement, it sometimes has some punning allusion to the owner's name. A device differs from a badge or cognizance primarily because it is a personal distinction, and not a badge borne by members of the same house successively. Heraldry is the profession, study, or art of devising, granting, and blazoning arms and ruling on questions of rank or protocol, as exercised by an officer of arms. Heraldry comes from Anglo-Norman herald, from the Germanic compound *harja-waldaz, "army commander". The word, in its most general sense, encompasses all matters relating to the duties and responsibilities of officers of arms. To most, though, heraldry is the practice of designing, displaying, describing, and recording coats of arms and badges. Historically, it has been variously described as "the shorthand of history" and "the floral border in the garden of history."The origins of heraldry lie in the need to distinguish participants in combat when their faces were hidden by iron and steel helmets. Eventually a formal system of rules developed into ever more complex forms of heraldry. The system of blazoning arms that is used in English-speaking countries today was developed by the officers of arms in the Middle Ages. This includes a stylised description of the escutcheon (shield), the crest, and, if present, supporters, mottoes, and other insignia. Certain rules apply, such as the Rule of tincture, and a thorough understanding of these rules is a key to the art of heraldry. The rules and terminology do differ from country to country, indeed several national styles had developed by the end of the Middle Ages, but there are some aspects that carry over internationally. Though heraldry is nearly 900 years old, it is still very much in use. Many cities and towns in Europe and around the world still make use of arms. Personal heraldry, both legally protected and lawfully assumed, has continued to be used around the world. Heraldic societies exist to promote education and understanding about the subject. The Macau Special Administrative Region (traditional Chinese: 澳門特別行政區; pinyin: Àomén Tèbié Xíngzhèngqū; Cantonese Yale: Oumun Dakbit Hangjeng Keui; Portuguese: Região Administrativa Especial de Macau), commonly known as Macau or Macao (pronounced /məˈkaʊ/, simplified Chinese: 澳门; traditional Chinese: 澳門; Mandarin Pinyin: Àomén; Jyutping: ou3 mun4), is one of the two special administrative regions of the People's Republic of China, the other being Hong Kong. Macau lies on the western side of the Pearl River Delta, bordering Guangdong province in the north and facing the South China Sea in the east and south.[6] The territory has thriving industries such as textiles, electronics and toys, and a noteable tourist industry. This makes it one of the richest cities in the world.[7] Macau was both the first and last European colony in China.[8][9] Portuguese traders first settled in Macau in the 16th century and subsequently administered the region until the handover on December 20, 1999. The Sino-Portuguese Joint Declaration and the Basic Law of Macau stipulate that Macau operates with a high degree of autonomy until at least 2049, fifty years after the transfer.[10] Under the policy of "one country, two systems", the Central People's Government is responsible for the territory's defence and foreign affairs, while Macau maintains its own legal system, police force, monetary system, customs policy, immigration policy, and delegates to international organisations and events. The recorded history of Macau can be traced back to the Qin Dynasty (221–206 BC), when the region now called Macau came under the jurisdiction of Panyu county, in the Nanhai prefecture of the province of Guangdong.[12] The first recorded inhabitants of the area were people seeking refuge in Macau from invading Mongols during the Southern Song Dynasty.[14] Under the Ming Dynasty (1368–1644 AD), fishermen migrated to Macau from Guangdong and Fujian provinces. But Macau did not develop as a major settlement until the Portuguese arrived in the 16th century.[15] In 1535, Portuguese traders obtained the rights to anchor ships in Macau's harbours and to carry out trading activities, though not the right to stay onshore.[16] Around 1552–1553, they obtained temporary permission to erect storage sheds onshore, in order to dry out goods drenched by sea water[17]; they soon built rudimentary stone houses around the area now called Nam Van. In 1557, the Portuguese established a permanent settlement in Macau, paying an annual rent of 500 taels of silver.[17] Ruins of St. Paul's Cathedral, by George Chinnery (1774–1852). The cathedral was built in 1602 and destroyed by fire in 1835. Only the southern stone façade remains today. Macau, ca. 1870 As more Portuguese settled in Macau to engage in trading, they made demands for self-administration; but this was not achieved until the 1840s.[18] In 1576, Pope Gregory XIII established the Roman Catholic Diocese of Macau.[19] In 1583, the Portuguese in Macau were permitted to form a Senate to handle various issues concerning their social and economic affairs under strict supervision of the Chinese authority,[20] but there was no transfer of sovereignty.[14] Macau prospered as a port but was the target of repeated failed attempts[21] by the Dutch to conquer it in the 17th century. Following the Opium War (1839–42), Portugal occupied Taipa and Coloane in 1851 and 1864 respectively. In 1887, the Qing government was forced to sign the Sino-Portuguese Treaty of Amity and Commerce, under which China ceded to Portugal the right of "perpetual occupation and government of Macau", and Portugal pledged to seek China's approval before transferring Macau to another country; Macau officially became a Portuguese colony.[14] In 1928, after the Qing Dynasty had been overthrown following the Xinhai Revolution, the Kuomintang (KMT) government officially notified Portugal that it was abrogating the Treaty of Amity and Commerce[22]; the two powers signed a new Sino-Portuguese Friendship and Trade Treaty in place of the abrogated treaty. Making only a few provisions concerning tariff principles and matters relating to business affairs, the new treaty did not alter the sovereignty of Macau and Portuguese government of Macau remained unchanged.[23] After the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949, the Beijing government declared the Sino-Portuguese Treaty of Amity and Commerce to be invalid as an “unequal treaty” imposed by foreigners on China. However, Beijing was not ready to settle the treaty question, leaving the maintenance of “the status quo” until a more appropriate time.[24] Influenced by the Cultural Revolution in mainland China and by general dissatisfaction with Portuguese government, riots broke out in Macau in 1966. In the most serious, the so-called 12-3 incident, 6 people were killed and more than 200 people were injured.[25][26] On January 28, 1967, the Portuguese government issued a formal apology. This marked the beginning of equal treatment and recognition of Chinese identity and of de facto Chinese control of the colony, as an official apology implicitly recognised that administration of Macau continued only as tolerated by the Communist government of the Chinese mainland.[26] Shortly after the overthrow of the Salazar dictatorship in 1974 in Lisbon, the new Portuguese government determined it would relinquish all its overseas possessions. In 1976, Lisbon redefined Macau as a "Chinese territory under Portuguese administration" and granted it a large measure of administrative, financial, and economic autonomy. Three years later, Portugal and China agreed to regard Macau as "a Chinese territory under (temporary) Portuguese administration".[14][27] The Chinese and Portuguese governments commenced negotiations on the question of Macau in June 1986. The two signed a Sino-Portuguese Joint Declaration the next year, making Macau a special administrative region (SAR) of China. The Chinese government assumed formal sovereignty over Macau on December 20, 1999.
Customer Reviews
4.9 out of 5 stars rating15.9K Total Reviews
15,871 Reviews
Reviews for similar products
5 out of 5 stars rating
By Deidre T.9 March 2023 • Verified Purchase
Post Card, Size: Standard Postcard, Paper: Signature Matte, Envelopes: None
Zazzle Reviewer Program
Exactly what I wanted, it is very difficult to acquire Vintage Australiana items. I am so please that I ordered 8 I will be using them for my scrap booking and Junk Journaling. Gorgeous, Zazzle produced and delivered exactly what I wanted.
5 out of 5 stars rating
By Deidre T.9 March 2023 • Verified Purchase
Post Card, Size: Standard Postcard, Paper: Signature Matte, Envelopes: None
Zazzle Reviewer Program
Way better quality than I ever expected. I love the colours, font and quality of the card. I'm so pleased I found Zazzle as it is near impossible to purchase Vintage or Retro Australian memorabilia online. I chose this design when I purchased them. They are perfect for my projects. I was very specific about what I wanted. I know where to come now when I need to order similar items.
5 out of 5 stars rating
By Michaela A.5 December 2022 • Verified Purchase
Post Card, Size: Standard Postcard, Paper: Signature Matte, Envelopes: None
Zazzle Reviewer Program
Perfect for the occasion I was using it for.
I was able to delete the lines so I could put in more wording.
Had an envelope so the address side wasn't necessary. Print quality and paper quality lovely.
Tags
Other Info
Product ID: 239395064156560310
Added on 10/10/09, 2:17 pm
Rating: G
Recently Viewed Items