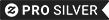Tap / click on image to see more RealViewsTM
The velvet details are simulated in the artwork. No actual velvet will be used in the making of this product.
$7.05
per badge
Czech Republic Official Coat Of Arms Heraldry 6 Cm Round Badge
Qty:
Shape
Round Badge
+$1.45
Size
Standard, 5.7 cm (2.25")
About badges
Sold by
About This Design
The velvet details are simulated in the artwork. No actual velvet will be used in the making of this product.
Czech Republic Official Coat Of Arms Heraldry 6 Cm Round Badge
Historically, they were used by knights to identify them apart from enemy soldiers. In Continental Europe, commoners were able to adopt burgher arms. Unlike seals and emblems, coats of arms have a formal description that is expressed as a blazon. In the 21st century, coats of arms are still in use by a variety of institutions and individuals (for example several universities have guidelines on how their coats of arms may be used and protect their use). The art of designing, displaying, describing and recording arms is called heraldry. The use of coats of arms by countries, states, provinces, towns and villages is called civic heraldry. In the heraldic traditions of England and Scotland an individual, rather than a family, had a coat of arms. In those traditions coats of arms are legal property transmitted from father to son; wives and daughters could also bear arms modified to indicate their relation to the current holder of the arms. Undifferenced arms are used only by one person at any given time. Other descendants of the original bearer could bear the ancestral arms only with some difference: usually a colour change or the addition of a distinguishing charge. One such charge is the label, which in British usage (outside the Royal Family) is now always the mark of an heir apparent. Because of their importance in identification, particularly in seals on legal documents, the use of arms was strictly regulated; few countries continue in this today. This has been carried out by heralds and the study of coats of arms is therefore called "heraldry". Some other traditions (e.g., Polish heraldry) are less restrictive — allowing, for example, all members of a dynastic house or family to use the same arms, although one or more elements may be reserved to the head of the house. In time, the use of coat of arms spread from military entities to educational institutes, and other establishments. According to a design institute article, "The modern logo and corporate livery have evolved from the battle standard and military uniform of mediaeval times". In his book, The Visual Culture of Violence in the Late Middle Ages, Valentin Groebner argues that the images composed on coats of arms are in many cases designed to convey a feeling of power and strength, often in military terms. The author Helen Stuart argues that some coat of arms were a form of corporate logo. Museums on mediaeval coat of arms also point out that as emblems they may be viewed as a pre-cursors to the corporate logos of modern society, used for group identity formation. The American Great Seal is often said to be the coat of arms of the United States. The blazon ("Paleways of 13 pieces, argent and gules; a chief, azure") is intentionally improper to preserve the symbolic number 13. Most American states generally have seals, which fill the role of a coat of arms. However, the state of Vermont (founded as the independent Vermont Republic) follows the American convention of assigning use of a seal for authenticating official state documents and also has its own separate coat of arms. Many American social fraternities and sororities, especially college organisations, use coats of arms in their symbolism. These arms vary widely in their level of adherence to European heraldic tradition. Organisations formed outside the United States with U.S. membership also may have a coat of arms. Roman Catholic dioceses and cathedrals have a coat of arms. Note that not all personal or corporate insignia are heraldic, though they may share many features. For example, flags are used to identify ships (where they are called ensigns), embassies and such, and they use the same colours and designs found in heraldry, but they are not usually considered to be heraldic. A country may have both a national flag and a national coat of arms, and the two may not look alike at all. For example, the flag of Scotland (St Andrew's Cross) has a white saltire on a blue field, but the royal arms of Scotland has a red lion within a double tressure on a gold (or) field. The Vatican has its own coat of arms. As the Papacy is not hereditary, its occupants display their personal arms combined with those of their office. Some Popes came from armigerous (noble) families; others adopted coats of arms during their career in the church. The latter typically allude to their ideal of life, or to specific Pontifical programmes.[11] A well known and widely displayed example in recent times was Pope John Paul II's coat of arms. His selection of a large letter M (for Mary) on his coat of arms was intended to express the message of his strong Marian devotion. Roman Catholic Dioceses also are assigned a coat of arms. A Basilica, or papal church also gets a coat of arms, which is usually displayed on the building. These may be used in countries which otherwise do not use heraldic devices. In Scotland, the Lord Lyon King of Arms has criminal jurisdiction to enforce the laws of arms. In England, Northern Ireland and Wales the use of arms is a matter of civil law and regulated from the College of Arms. In reference to a dispute over the exercise of authority over the Officers of Arms, Arthur Annesley, 1st Earl of Anglesey, Lord Privy Seal, declared on 16 June 1673 that the powers of the Earl Marshal were "to order, judge, and determine all matters touching arms, ensigns of nobility, honour, and chivalry; to make laws, ordinances, and statutes for the good government of the Officers of Arms; to nominate Officers to fill vacancies in the College of Arms; to punish and correct Officers of Arms for misbehaviour in the execution of their places". It was further declared that no patents of arms or any ensigns of nobility should be granted and no augmentation, alteration, or addition should be made to arms without the consent of the Earl Marshal. Today, the term "coat of arms" is frequently applied in two different ways. In some uses, it may indicate a full achievement of arms or heraldic achievement, which includes a variety of elements — usually a crest sitting atop a helmet, itself sitting on a shield; other common elements include supporters holding up the shield and a motto (beneath in England, above in Scotland). Some people wrongly use "coat of arms" or "arms" to refer to the escutcheon (i.e., the shield itself), or to one of several designs that may be combined in one shield. (Note that the crest is one specific part of a heraldic achievement and that "crest of arms" is a misnomer.) The "coat of arms" frequently are adorned with a device - a motto, emblem, or other mark used to distinguish the bearer from others. If a motto is a part of the achievement, it sometimes has some punning allusion to the owner's name. A device differs from a badge or cognizance primarily because it is a personal distinction, and not a badge borne by members of the same house successively. Heraldry is the profession, study, or art of devising, granting, and blazoning arms and ruling on questions of rank or protocol, as exercised by an officer of arms. Heraldry comes from Anglo-Norman herald, from the Germanic compound *harja-waldaz, "army commander". The word, in its most general sense, encompasses all matters relating to the duties and responsibilities of officers of arms. To most, though, heraldry is the practice of designing, displaying, describing, and recording coats of arms and badges. Historically, it has been variously described as "the shorthand of history" and "the floral border in the garden of history."The origins of heraldry lie in the need to distinguish participants in combat when their faces were hidden by iron and steel helmets. Eventually a formal system of rules developed into ever more complex forms of heraldry. The system of blazoning arms that is used in English-speaking countries today was developed by the officers of arms in the Middle Ages. This includes a stylised description of the escutcheon (shield), the crest, and, if present, supporters, mottoes, and other insignia. Certain rules apply, such as the Rule of tincture, and a thorough understanding of these rules is a key to the art of heraldry. The rules and terminology do differ from country to country, indeed several national styles had developed by the end of the Middle Ages, but there are some aspects that carry over internationally. Though heraldry is nearly 900 years old, it is still very much in use. Many cities and towns in Europe and around the world still make use of arms. Personal heraldry, both legally protected and lawfully assumed, has continued to be used around the world. Heraldic societies exist to promote education and understanding about the subject. The Czech Republic en-us-Czech Republic.ogg /ˈtʃɛk rɨˈpʌblɪk/ (help·info)[3] (Czech: Česká republika, pronounced [ˈtʃɛskaː ˈrɛpuˌblɪka] (Speaker Icon.svg listen), short form Česko [ˈtʃɛskɔ]) is a landlocked country in Central Europe.[4][5] The country borders Poland to the northeast, Germany to the west and northwest, Austria to the south and Slovakia to the east. The capital and largest city is Prague (Czech: Praha). The country is composed of the historic regions of Bohemia and Moravia, as well as parts of Silesia. The Czech Republic has been a member of NATO since 1999 and of the European Union since 2004. From 1 January 2009 to 1 July 2009, the Czech Republic held the Presidency of the Council of the European Union. Following the Battle of Mohács in 1526, the Czech lands fell under Habsburg rule, becoming part of the Austrian Empire in 1804 and of Austria–Hungary in 1867. The independent Republic of Czechoslovakia was formed in 1918, following the collapse of the Austro-Hungarian empire after World War I. After the Munich Agreement, German occupation of Czechoslovakia and the consequent disillusion with the Western response and gratitude for the liberation of the major portion of Czechoslovakia by the Red Army, the Communist party won plurality (38%)[6] in the 1946 elections. In a 1948 coup d'état, Czechoslovakia became a communist-ruled state. In 1968, the increasing dissatisfaction culminated in attempts to reform the communist regime. The events, known as the Prague Spring of 1968, ended with an invasion by the armies of the Warsaw Pact countries (with the exception of Romania); the troops remained in the country until the 1989 Velvet Revolution, when the communist regime collapsed. On 1 January 1993, Czechoslovakia peacefully dissolved into its constituent states, the Czech Republic and Slovakia. The Czech Republic is a pluralist multi-party parliamentary representative democracy. President Václav Klaus is the current head of state. The Prime Minister is the head of government (currently Jan Fischer). The Parliament has two chambers: the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate. It is also a member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the Council of Europe and the Visegrád Group. The Czech Republic made economic reforms such as fast privatisations. Annual gross domestic product growth has recently been around 6%. The country is the first former member of the Comecon to achieve the status of a developed country (2006), according to the World Bank.[7] The Czech Republic also ranks top among the former Comecon countries in the Human Development Index.
Customer Reviews
4.8 out of 5 stars rating8.6K Total Reviews
8,585 Reviews
Reviews for similar products
5 out of 5 stars rating
By Siti H.6 August 2022 • Verified Purchase
Round Badge, Standard, 5.7 cm (2.25")
Zazzle Reviewer Program
This badge I ordered for my work mate. It’s so cute and perfectly done. I’m very happy with how it’s turn out. Thanks. The color was exactly as the picture on the advertisement. It is good quality print, for the price I paid, I’m very happy with the product. Thanks so much.
5 out of 5 stars rating
By Ah F.17 November 2019 • Verified Purchase
Round Badge, Standard, 5.7 cm (2.25")
Zazzle Reviewer Program
The product looks so beautiful!!! Thank you so much, you did a great job printing it. It has everything I ever wanted and the shiny finish is just perfect. The metal back really complements the picture. Thank You! ;). The image was great. All the colours were there and the writing was readable.
5 out of 5 stars rating
By Anonymous26 December 2025 • Verified Purchase
Round Badge, Standard, 5.7 cm (2.25")
Perfect. Received looking exactly as it was meant to. Love it. .
Tags
Other Info
Product ID: 145526309357865861
Added on 9/10/09, 6:27 pm
Rating: G
Recently Viewed Items